Use Sra Toolkit
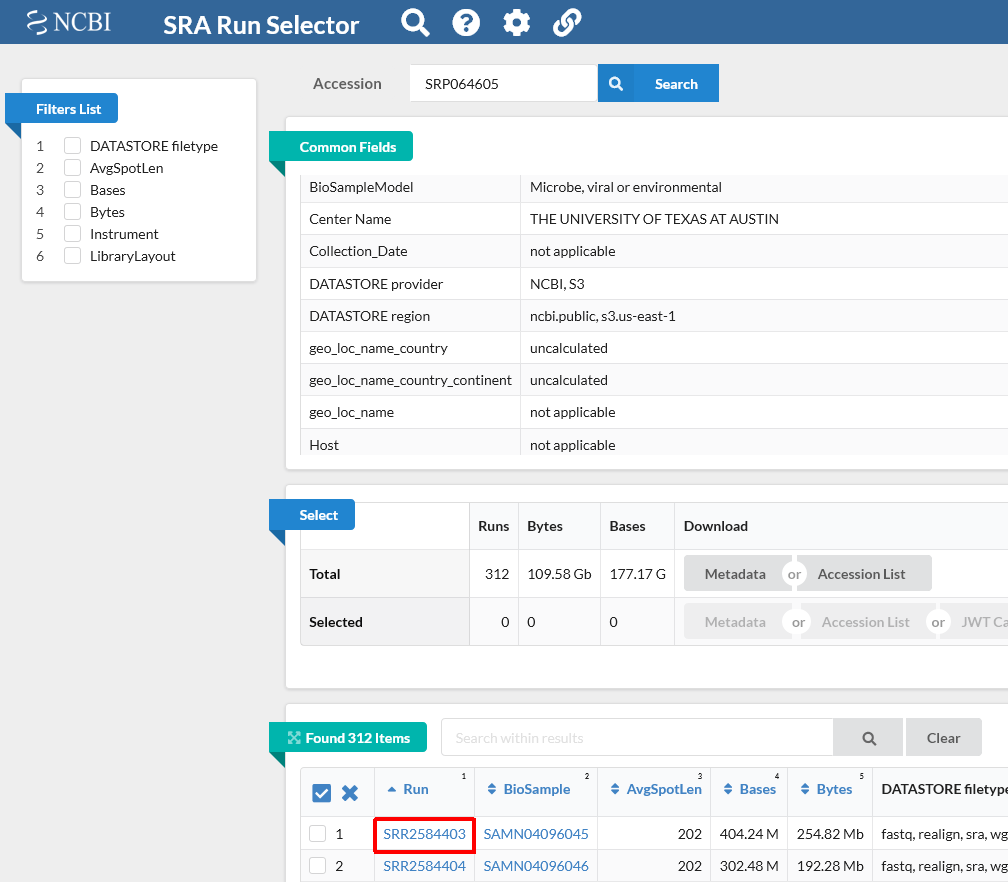
The SRA Toolkit and SDK from NCBI is a collection of tools and libraries for using data in the INSDC Sequence Read Archives. Much of the data submitted these days contain alignment information, for example in BAM, Illumina export.txt, and Complete Genomics formats. With aligned data, NCBI uses Compression by Reference, which only stores the. SRA Toolkit is NCBI download.sra file and conversion. Extreme tool for FASTQ file Download compressed package. First, go to the NCBI official website, click Download- Download Tools, find SRA Toolkit, click Download, find the version that suits you, I am Ubuntu Linux64 bit, copy the link, with Wget download on the server. Download and convert SRA files to FASTQ files using the NCBI’s SRA toolkit. Use a Python script to batch download files with the SRA prefetch and fastq-dump tools. Finding raw sequencing data in GEO.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Security Rule requires that covered entities and its business associates conduct a risk assessment of their healthcare organization. A risk assessment helps your organization ensure it is compliant with HIPAA’s administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. A risk assessment also helps reveal areas where your organization’s protected health information (PHI) could be at risk. To learn more about the assessment process and how it benefits your organization, visit the Office for Civil Rights' official guidance.
What is the Security Risk Assessment Tool (SRA Tool)?

May 30, 2021 Download SRA datasets using NCBI SRA toolkit. Note: Current SRA toolkit version 2.10.8 does not support Aspera client (ascp). Even though ascp can run with older versions, it will download the data by https mode and not by FASP mode. Jul 07, 2021 Use SRA Toolkit tools to directly operate on SRA runs. NCBI blocks any connection from computing nodes because they are behind firewalls. Thus OSC users cannot use SRA tools to download data 'on-the-fly' at runtime or fetch data on computing nodes, e.g. 'fastq-dump -X 5 SRR390728' or 'prefetch SRR390728'.
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), in collaboration with the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR), developed a downloadable Security Risk Assessment (SRA) Tool to help guide you through the process. The tool is designed to help healthcare providers conduct a security risk assessment as required by the HIPAA Security Rule and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Service (CMS) Electronic Health Record (EHR) Incentive Program.
All information entered into the SRA Tool is stored locally to the users’ computer or tablet. HHS does not receive, collect, view, store or transmit any information entered in the SRA Tool. The results of the assessment are displayed in a report which can be used to determine risks in policies, processes and systems and methods to mitigate weaknesses are provided as the user is performing the assessment. The target audience of this tool is medium and small providers; thus, use of this tool may not be appropriate for larger organizations.
The updated version of the popular Security Risk Assessment (SRA) Tool was released in October 2018 to make it easier to use and apply more broadly to the risks of the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of health information. The tool diagrams HIPAA Security Rule safeguards and provides enhanced functionality to document how your organization implements safeguards to mitigate, or plans to mitigate, identified risks. The new SRA Tool is available for Windows computers and laptops.
The tool is now more user friendly, with helpful new features like:
- Enhanced user interface
- Modular workflow
- Custom assessment logic
- Progress tracker
- Threats & vulnerabilities rating
- Detailed reports
- Business associate and asset tracking
- Overall improvement of the user experience
For details on how to use the tool, download the SRA Tool 3.2 User Guide [PDF - 4.8 MB].
Legacy Version: Security Risk Assessment Tool Version 2.0
Use Sra Toolkit
Still using the old version of the tool? Note that you can’t directly transfer data from 2.0 to 3.0, but can upload certain portions (e.g., lists of assets and BAs). Refer to the SRA Tool User Guide 2.0 [PDF - 4.5 MB]* for more information.

Paper-based version of the SRA 2.0 tool is also available:
*Persons using assistive technology may not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, contact ONC at PrivacyAndSecurity@hhs.gov
The Security Risk Assessment Tool at HealthIT.gov is provided for informational purposes only. Use of this tool is neither required by nor guarantees compliance with federal, state or local laws. Please note that the information presented may not be applicable or appropriate for all health care providers and organizations. The Security Risk Assessment Tool is not intended to be an exhaustive or definitive source on safeguarding health information from privacy and security risks. For more information about the HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules, please visit the HHS Office for Civil Rights Health Information Privacy website.
NOTE: The NIST Standards provided in this tool are for informational purposes only as they may reflect current best practices in information technology and are not required for compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule’s requirements for risk assessment and risk management. This tool is not intended to serve as legal advice or as recommendations based on a provider or professional’s specific circumstances. We encourage providers, and professionals to seek expert advice when evaluating the use of this tool.
The Sequence Read Archive (SRA), NCBI’s largest growing repository of molecular data, archives raw sequencing data and alignment information from high-throughput sequencing platforms, including Roche 454 GS Systems®, Illumina’s Genome Analyzer®, and Complete Genomics® systems.
See Full List On Osc.edu
Researchers commonly use SRA data to make discoveries via comparison of data sets. Data sets can be compared through the SRA web interface, but if you want to integrate these downloads and file conversions into an already existing pipeline, or you simply prefer using a command-line interface, we recommend using the SRA Toolkit.
Figure 1. The SRA Toolkit and GitHub download pages.
This open-source toolkit can be downloaded from the SRA Toolkit webpage or from GitHub/NCBI and is available for the major operating systems. The GitHub web link also provides the uncompiled files for you if you are computer savvy and would like to compile the files yourself. No matter where you download the toolkit from, there are instructions for installation and use as well as an FAQ page.
The toolkit’s command-line executables allow you to stream data from the NCBI/SRA servers for direct analysis or transform the data into common text formats, such as FASTQ or SAM. After applying for access, users can also get restricted-access data from dbGaP, with functions for decrypting and encrypting metadata (for example, phenotype data). Since some of these data files can be exceptionally large, the command-line tools make downloading them that much easier.
SRA Toolkit can also be used to run BLAST searches against archived NGS data. The application allows users to compare a FASTA sequence of interest against specific SRA accessions. For example, if you have a set of run accessions (indicated in the command by ‘ERR’ accession numbers), and you want to search for a particular FASTA sequence, the code would look like the following:
where “nt.test” is the FASTA sequence of interest and “test.out” is the output file after the search containing the results.
An important note: When running this function, the FASTA file query must be located inside the bin directory in the SRA Toolkit to use the command format above. Otherwise, a file path to the blast function must be specified instead.
We hope you’ll find this resource helpful and beneficial to your research needs. If you have questions or comments regarding the SRA Toolkit, please email sra@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov and we’d be happy to help!